Arthritis is of three types:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
Among all three types, osteoarthritis is a prevalent condition affecting your joints, such as the knees, shoulder, hips, feet, and hands.
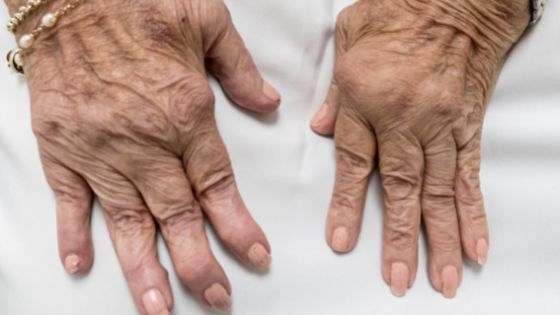

What is osteoarthritis?
Cartilage is aharsh, smooth, slippery coat covering the bone surface. It is this cartilage structure that helps your bones to move quickly against each other.
What if this part of cartilage becomes thin? The bone surface turns rougher. Moreover, it will become impossible for the bones to move quickly. Hence, these joint regions get affected and develop osteoarthritis.
What happens if the cartilage becomes thin? Are there any signs?
If damage occurs in your cartilage, the tissues within the joint part perform vigorously to heal that damage. This vigorous healing process may even alter the structure of your joint.
During this process, you experience pain in your joint region, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty in joint mobility. In severe cases, you may even find an extra bone development at the edge of your joint. This extra bone development is called osteophytes. These outgrowths will stop your mobility by rubbing against the adjacent regions.
Additionally, the joint capsule lining, otherwise called synovium, may become thick and release more fluid, which will swell up the joint part.
These joint regions cannot move quickly and develop grading or cracking sounds. Furthermore, the joint structure will lose its stability, weakening the adjacent muscles.
As we grow older, many develop osteoarthritis, and we remain unaware of it. The extent of this joint damage can figure out the severity of pain and mobility problems.
What exactly causes osteoarthritis?
If you think about the cause of osteoarthritis, the quick answer will be ‘wear and tear’. Still, the risk of getting osteoarthritis depends on the factors given below:
- Heredity – Alteration of genes that control the collagen protein may develop osteoarthritis early.
- Age –You usually get osteoarthritis in the late 40s. During this period, your body will undergo significant changes such as weight gain, weakening of muscles, and reduced self-healing ability.
- Gender – Osteoarthritis is more common and usually severe in women than men.
- Obesity (Weight gain) – Obesity is the primary risk factor, especially in weight-bearing joints such as the knee and hip.
- Joint abnormalities and injuries– Repetitive activities and some sports injuries can also cause osteoarthritis joint injuries. Other joint problems such as rheumatoid arthritis and gout can also cause osteoarthritis.
- Weather condition–Weather conditions or changes like a fall in atmospheric pressure do not cause arthritis symptoms. However, they may worsen your arthritis symptoms, especially your pain.
What are the regions affected by osteoarthritis?
All your joints can develop osteoarthritis. Still, osteoarthritis commonly affects your shoulder, knee, elbow, hip, wrist, thumb, spine, ankle, foot, back, neck, jaw (temporomandibular joint), and big toes.
How can you diagnose osteoarthritis?
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis is mandatory before proceeding with its treatment. Only then you can figure out the right course of treatment.
The physician will diagnose your condition and its severity based on the following procedures:
Symptomatic study – the initial point and the degree of severity of these symptoms
Physical examination
- Level of joint pain
- Degree of restriction in movements
- The intensity of bone swelling
- Weakness of adjacent muscles around the affected joint
- Joint instability
- Crepitus sensation (creaking or grating sensation of the joint region), if any
X-ray examination to evaluate whether there is any calcium deposition in the joint area
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) examination to figure out the possible joint or bone problems that may cause the symptoms mentioned above
Is there any treatment for osteoarthritis condition?
Yes. Few conventional treatment methods can help in managing your osteoarthritis symptoms.
- Home treatment (R.I.C.E. formula) – R.I.C.E. stands for Rest, Ice application, Compression, and Elevation.Take proper rest. Apply ice packs to the affected area. Wear compression bands to limit the mobility of the affected joint part. Always place the affected joint in the raised position above your chest level while resting.
- Activity modification – Make sure to change the routine tedious activities till you get relief from arthritis symptoms. For example, if you run a lot, try to stop running until your pain decreases. Still, you can continue walking instead of running to lead an active life.
- Physical therapy – Physical therapy, which includes aerobic exercises, range of movement exercises, strengthening exercises, and hydrotherapy, can help you get adequate relief from osteoarthritis symptoms. Even cycling, walking, and swimming can help people can also work.
- NSAIDs administration – Consumption of NSAIDs (Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) can help reduce inflammation, pain, and swelling. Still, doctors do not prescribe them for a more extended period due to their significant complications like gastrointestinal problems, cardiovascular issues, and kidney ailments.
- Corticosteroid injections – Physicians also suggest corticosteroid injections if medications do not help. Still, repetitive use of steroids for a longer duration can deteriorate the tendon strength around the affected joint region.
- Surgery – Physicians opt for surgery as the final option to treat osteoarthritis.
The surgical options include:
- Arthroscopic keyhole surgery to eliminate loose bone fragments from the affected joint region
- Joint fusion – The joints are fixed together to stop further movements.
- Joint replacement surgery
Still, osteoarthritis patients do not choose surgery right away due to its prolonged post-surgical rehabilitation session. So, before proceeding with surgery, these patients want to make sure that they try all non-surgical options. This is where regenerative treatment can help you!
How Regenerative Medicine Can Help to Heal Your Arthritis
Regenerative medicine includes prolotherapy, PRP (Platelet-rich plasma), and stem cell therapy such as Bone Marrow Aspiration Concentration (BMAC), Stromal Vascular Fraction (SVF), Autologous Plasma concentrate, and many more.
Compared to the above-given conventional treatment methods, regenerative medicine performs uniquely. It treats the underlying cause of the symptoms to get rid of symptoms immediately. With the help of a physiotherapist, this healing can be expedited.
Regenerative treatment is a novel revolutionary method where doctors use patients’ body cells to treat them. Hence, they do not experience any allergy or rejection problems.
Patients need not stay in hospitals for a long duration; hence no hospitalization is needed. This minimally invasive treatment involves only a short recovery time with a long-lasting effect. It is safe, effective, and natural.
Takeaway
Living with osteoarthritis can even make you emotionally weak. If this continuous nagging pain ruins your sleep, affecting your mood and body metabolism.
Contact Medica Stem Cells Clinic immediately and schedule a consultation if you feel low. Our medical team is available to listen to your problems and provide the appropriate solution without making you suffer more.
Hence, talk to us as early as possible to know whether you can also lead a long-lasting pain-free life without any surgery.