Hair loss is a common condition that affects both women and men. About 60% of men and 50% of women worldwide experience hair loss. Most cases of hair loss resulting from ageing, but other factors such as stress, genetics, lifestyle, trauma, and certain medications may lead to hair loss.
Some people opt for OTC drugs and topical treatments such as Minoxidil and Finasteride to reverse or stop hair loss, but these may not give a permanent result. Hair transplant treatment, on the other hand, can permanently restore lost or thinning hair.
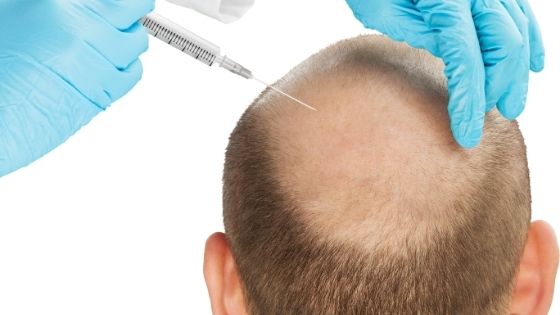

Hair transplant treatment is a common hair restoration option where the surgeon will remove hair from a donor site and implant them in a balding area. If you want to have a hair transplant, consulting your doctor is important, but you also need to get more information about the condition to make an informed decision.
Who is eligible for a hair transplant?
To determine your suitability for hair transplant surgery, you need to visit a hair transplant surgeon. The surgeon will assess your hair loss’s severity, type, and pattern. The surgeon will also check the quantity and quality of hair on the donor area, including the size of the balding area. The donor’s hair is usually from the back of the head, where hair growth is fuller.
The surgeon will also ensure you do not have a health condition that may cause complications during or after the hair transplant. Although a hair transplant is a minimally invasive surgery, it has some risks.
The surgeon will explain what you should expect and what the treatments involve.
What are the common hair transplant procedures?
Direct hair implantation (DHI), Follicular unit transplantation (FUT), and follicular unit extraction (FUE) are the most common hair transplant procedures. Different important factors such as the size of the balding area, quantity and quality of the donor’s hair, and type of hair loss will determine the most suitable hair transplant procedure.
Follicular unit extraction (FUE)
During FUE hair transplant, the surgeon will shave the hair on the donor area, usually the back of the head, and extract the hair follicles using a microneedle. The procedure is minimally invasive and doesn’t require skin grafts. With FUE, scaring is limited, so you won’t worry about linear scars.
The hair transplant surgeon will make small incisions on the recipient areas for the hair transplantation. The FUE transplant procedure is less invasive than the FUT transplant procedure.
Follicular unit transplantation (FUT)
In FUT, the hair transplant surgeon will remove a long strip of skin from your scalp on the donor area and then cut the strip into 500 – 2000 follicular units. Each follicular unit has several hair strands. The surgeon will transplant each unit into the incisions made on the recipient area. The surgeon will stitch the area where they extracted the skin strip.
Direct hair implantation (DHI)
DHI technique leaves fewer scars and is less painful than FUE and FUT. It involves having the hair from the donor area, and then the surgeon will extract each hair follicle and load them into a specialised pen-shape tooth, known as a DHI implanter.
The implanter places the hair follicles directly into the balding area on your scalp. This procedure gives a more natural look and requires the expertise of an experienced hair surgeon.
If you want to undergo hair transplant surgery and need a sapphire hair clinic in Istanbul, visit Turkey Hair Transplant. Our experienced hair transplant surgeon will ensure you have a natural-looking result and a safe recovery.
Frequently asked questions on hair transplant surgery
Do I need anaesthesia during the procedure?
Hair transplant treatment is done under local anaesthesia, but some clinics also offer patients a sedative to help them relax during the hair transplant. This reduces the risk of discomfort or pain during the procedure.
What is the recovery process?
After the surgery, the surgeon will bandage the donor site, which you will remove after 1 – 2 days. If your surgery involves stitches, you will visit the clinic within 7 – 10 days to remove them.
You may notice swollen or tender gums post-surgery. Your doctor may recommend medications to relieve the discomfort. Your doctor will also recommend anti-inflammatory medications and antibiotics to ease the swelling and prevent infection.
Following your doctor’s instructions is important, and you also need a healthy diet to strengthen the implanted hair follicles. Eating healthy foods will also aid in faster recovery.
The following nutrients are essential for your hair growth.
- Zinc
Enhances hormonal balance, cell proliferation, and tissue repair
- Vitamin B
B-complex such as B7 and B12 play a vital role in healthy hair growth, structure, and quality.
- Iron
Iron improves hair texture and strengthens hair. It also aids oxygen and nutrient transportation to the scalp and hair follicles.
What are the necessary precautions post-hair transplant?
After hair transplant surgery, you can resume your regular activities, usually within 2 – 5 days. But, you have to take certain precautions and adhere to the aftercare tips for a successful treatment and better results.
Avoiding things that cause exertions and strenuous activities, such as working out for about 2 – 3 weeks following your surgery, is necessary. Other precautions are:
- Avoid combing over the grafts for about three weeks after the procedure
- Avoid direct exposure to sunlight in the first two months
- Avoid washing your hair the first few days after the procedure
- Avoid saunas and steam baths in the first two months
- Use only mild shampoo to wash your hair in the first couple of weeks
- Adhere to your doctor’s advice for adequate healing
How much is hair transplant surgery?
The cost of hair transplant treatment varies depending on the procedure you want to undergo, the surgeon’s expertise, your location, and the size of the balding area.
Generally, you can have a hair transplant procedure for between £3000 and £11,000.






















